Maximizing Data Sync and Collaboration with Azure Storage Sync Services
In today’s digital landscape, efficient data synchronization and seamless collaboration are paramount for businesses to stay competitive. Enterprises are constantly seeking ways to centralize their data, streamline access, and optimize storage capacity. This is where Azure Storage Sync Services steps in, offering a robust solution to effortlessly synchronize and collaborate on data across various locations.
However, effectively implementing and managing Azure Storage Sync Services can be a complex endeavor. That’s where Cloudologix comes into play. As a leading provider of cloud solutions and expertise, Cloudologix brings a wealth of experience in harnessing the full potential of Azure Storage Sync Services.
“Optimizing Data Collaboration: Unleashing the Potential of Azure Storage Sync Services with Cloudologix “

Azure File Sync Management Concepts
Sync groups are deployed into Storage Sync Services, which are top-level objects that register servers for use with Azure File Sync and contain the sync group relationships. The Storage Sync Service resource is a peer of the storage account resource, and can similarly be deployed to Azure resource groups. A Storage Sync Service can create sync groups that contain Azure file shares across multiple storage accounts and multiple registered Windows Servers.
Here are some key features and benefits of Azure Storage Sync Services:
- Hybrid storage: Azure Storage Sync Services enables organizations to maintain a hybrid storage model, where some data is stored in the cloud and some on-premises.
- Sync capabilities: Azure Storage Sync Services provides bidirectional synchronization of files between on-premises servers and Azure file shares, which means that changes made on either side are automatically synchronized to the other.
- Cloud tiering: Azure Storage Sync Services also provides a cloud tiering feature, which allows organizations to automatically move infrequently accessed files to the cloud to free up on-premises storage space.
- Disaster recovery: Azure Storage Sync Services can also be used to create a disaster recovery solution, as it enables organizations to replicate their on-premises files to Azure and failover to Azure in the event of a disaster.
- Scalability: Azure Storage Sync Services can scale up or down based on the needs of the organization, making it a flexible and cost-effective solution for managing file services.
- Security: Azure Storage Sync Services provides security features such as encryption in transit and at rest, role-based access control (RBAC), and Azure AD authentication to ensure the confidentiality and integrity of data.
- Performance: Azure Storage Sync Services uses a distributed architecture to optimize performance and reduce latency when synchronizing files between on-premises and cloud-based environments.
Overall, Azure Storage Sync Services can help organizations to simplify their storage management, reduce costs, and improve data availability and disaster recovery capabilities.
Components of Azure File Sync Service
- Storage Sync Service
This is the first and top-level component (Resource) for Azure file sync. It enables synchronization of files between an Azure File share and an on-premises Windows Server. It is used to manage sync relationships between multiple on-premises servers and Azure file shares associated with different storage accounts within a single subscription.
- Sync Group
A sync group is a feature of Azure Storage Sync Services that enables synchronization of files between an Azure file share and one or more on-premises servers. It is a logical container that defines the sync relationship between the Azure file share and the registered server endpoints.
- Registered Server
A registered server is a Windows Server that has been configured to synchronize files with an Azure file share using Azure Storage Sync Services.
When a server is registered, it establishes a connection to the Azure Storage Sync Service, which facilitates synchronization of files between the server and the Azure file share.
Once a server is registered, it becomes a part of the sync group, and changes made to files and directories on the server are automatically synced with the Azure file share, and vice versa. Multiple servers can be registered to a sync group, allowing for synchronization across multiple servers and environments.
- Azure File Sync Agent
The Azure File Sync Agent is a software component that is installed on a Windows Server to enable synchronization of files between the server and an Azure file share using Azure Storage Sync Services.
The agent continuously monitors changes made to files and directories on the server and automatically syncs those changes with the Azure file share. It also provides local caching of frequently accessed files to improve performance and reduce network usage.
- Server Endpoint
A server endpoint is a representation of a folder on a registered Windows Server that is synchronized with an Azure file share using Azure Storage Sync Services.
When a server endpoint is created, it establishes a direct link between a specific folder on the registered server and a specific location in the Azure file share. This enables files and directories stored in the server folder to be synchronized with the corresponding folder in the Azure file share and vice versa.
- Cloud Endpoint
When adding an Azure file share to a sync group as a cloud endpoint, there are two options to consider if the file share already contains data (files): merge or authoritative. If we want to download these files to the server endpoint, we should select the merge option. This will enable us to combine any existing files with the ones on the server endpoint. However, if we want to overwrite any files with the same name and path on the file share, we should choose the authoritative option. It is important to note that selecting the authoritative option for the new file share will do nothing but if it contains data then it will replace any data on the file share with the same name and path, so it should be used with caution.
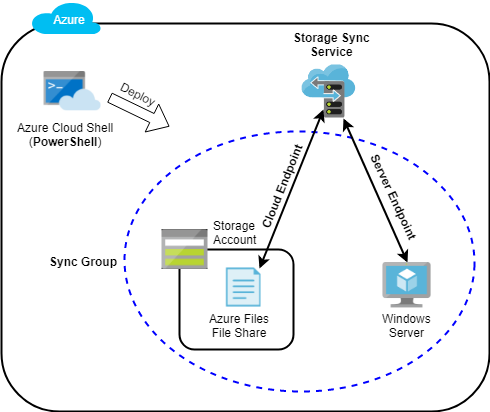
Configuring Sync Group in Azure File Sync:
Step-by-Step Guide
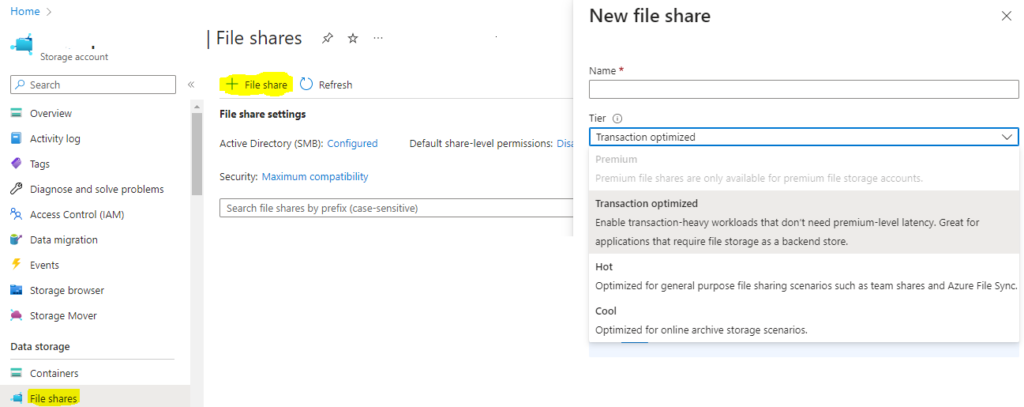
Step-1. Create Azure File Share
Create a file share by giving it to the appropriate and select appropriate tier: Hot.
Step-2: Create Windows VM
To demonstrate synchronization within the Azure environment, you can create a Windows virtual machine (VM) in Azure. This VM will serve as the server endpoint, actively participating in the synchronization process with an Azure file share acting as the cloud endpoint.
If you wish to synchronize data from your on-premises infrastructure, ensure you have a Windows Server running at your on-premises location. This server will seamlessly integrate with Azure File Sync, enabling synchronization between your on-premises data and the cloud.
By establishing this synchronization setup, you can efficiently manage and transfer files, ensuring data consistency and availability across both your Azure environment and on-premises infrastructure.
Step-3: Create Storage Sync service.
To create Storage sync service in the search bar, type “Storage Sync Service” and select the “Storage Sync Service” option from the search results provide all the information required in Basic and Networking Tab to create the Storage Sync Service.
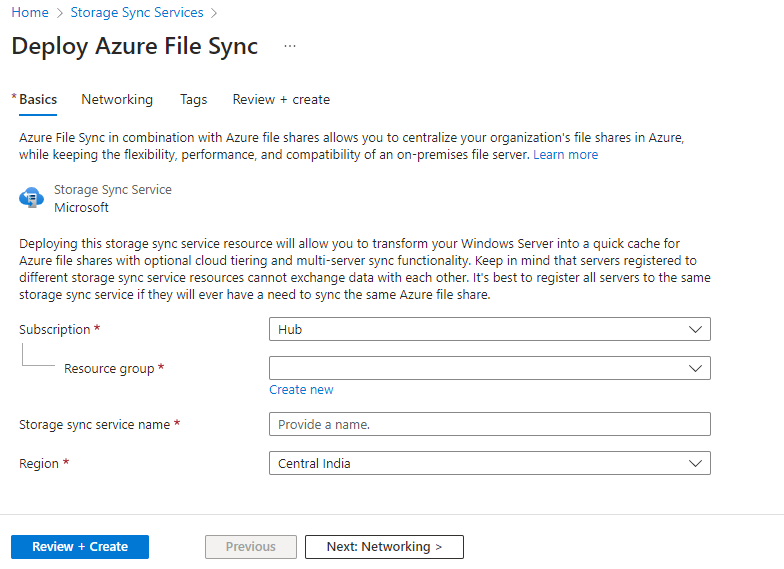
Note: – When creating a storage sync service, it’s important to keep in mind that the file sync service must be in the same region as the storage account.
Some Common Errors and their Resolution
- “Endpoint is not accessible” error: This error indicates that the server endpoint or the cloud endpoint is not accessible due to network or connectivity issues. To resolve this, check the network connectivity between the endpoints, ensure that the endpoints are online and reachable, and verify that any firewall or network security groups allow the necessary traffic.
- “Sync metadata corruption” error: This error occurs when the synchronization metadata associated with a file or folder becomes corrupted. It can lead to synchronization failures or inconsistencies. To address this, you can reset the sync metadata for the affected files or folders by deleting and re-creating the server endpoint or cloud endpoint. Be cautious as this action will initiate a full sync of the affected files.
- “Insufficient disk space on server” error: This error occurs when the server endpoint does not have enough disk space to accommodate the synchronized files. Check the available disk space on the server and ensure that it meets the requirements for the synchronized data. If needed, free up disk space or allocate additional storage to the server to resolve the issue.
- “Insufficient cloud tiering storage quota” error: If you have enabled Cloud Tiering, you may encounter this error when you exceed the storage quota allocated for tiered files in the Azure storage account. To resolve this, increase the storage quota for the Azure storage account or adjust the tiering policies to control which files are tiered and optimize the storage usage.
Conclusion
In summary, Azure File Sync simplifies file synchronization between on-premises servers and the Azure cloud. By carefully planning and configuring Azure File Sync, optimizing performance, and addressing any encountered errors, you can achieve efficient file synchronization, seamless collaboration, and enhanced data availability across your infrastructure. For further assistance and guidance, reach out to Cloudologix Support, your trusted cloud provider, and take full advantage of Azure File Sync capabilities

